【Reprinted article】
In the current epidemic situation, it is difficult to find a "mask". Under such circumstances, medical protective masks, medical surgical masks, disposable medical masks, N95 protective masks and other types of masks have become in short supply. What is the difference between different types of masks? What are the standards for masks? How should you choose? Is a knitted mask considered a mask? Are antibacterial masks really antibacterial? Recently, we specially invited Professor Gong Yan from the School of Materials Design and Engineering of Beijing Institute of Fashion Technology to give you a detailed interpretation.
Professor Gong Yan is currently working at Xinjiang Tarim University to prepare for the establishment of the Textile and Clothing College. His team has participated in the development of many masks, has many national patents, and has won the National Invention Gold Award. Professor Gong's team at the Beijing Institute of Fashion Technology is currently working on the development of high-performance composite fiber cloth and antibacterial mask technology and testing and evaluation research. The main contents of this project include: melt-blown process optimization of high-charge fiber membranes, the relationship between composite fiber properties and air resistance and filtration efficiency, performance evaluation of new renewable composite fiber cloths, and the application of antibacterial composite functional materials in masks.
1. Mask materials, structure and working principle
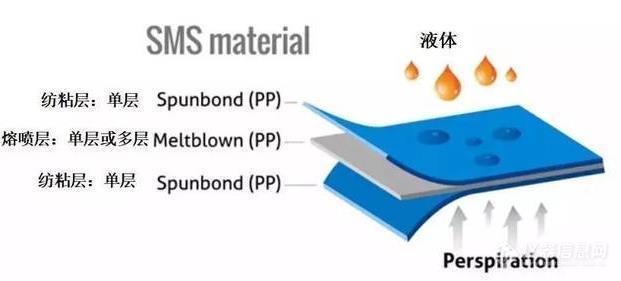
Mask Material:
Medical masks are generally made of three layers of non-woven fabrics, namely: spunbond non-woven fabrics, meltblown non-woven fabrics, and spunbond non-woven fabrics. The outer layer of the mask has a water-blocking effect, the middle layer is filtering, and the inner layer is hygroscopic. Non-woven fabric is a kind of fabric that does not require spinning and weaving. It is not interwoven and knitted together by yarns one by one, but the fibers are directly bonded together by physical methods. Spunbond non-woven fabrics and meltblown non-woven fabrics are both a type of "non-woven fabric". Meltblown non-woven fabrics are characterized by fine fiber diameter and large specific surface area, which can filter particles in the air well, but have low strength and poor wear resistance. Spunbond fabrics have a large fiber line density, and the fiber web is composed of continuous filaments. Its high strength can just make up for the shortcomings of meltblown fabrics.
Working principle: Taking a medical surgical mask (ordinary 3-layer flat non-woven mask) as an example, the structure includes an outer layer of non-woven fabric to prevent splashing liquids and large particles; a middle layer of electrostatic melt-blown non-woven fabric (polypropylene), that is, a charged layer, which uses electrostatic adsorption to effectively block tiny particles, especially particles or droplets carrying nano-scale viruses, to achieve effective blocking of viruses and other particles; the inner layer of non-woven fabric is used to block exhaled water vapor. The principle of mask filtration is mainly to use electrostatic adsorption and fiber arrangement to block fine particles and droplets. The charged layer in the middle of the mask plays an important role in protecting against particles or droplets carrying viruses, bacteria, etc. During the use of the mask, the static electricity of the charged layer disappears due to the deposition of bacteria, viruses and particles in the electrostatic layer and the breath (water vapor), which significantly damages its filtration effect, especially the effective blocking of particles such as viruses. In an emergency, if you want to reuse the mask, you need to focus on two points: one is how to kill and remove bacteria and viruses deposited on the mask; the other is how to replenish static electricity for the middle charged layer. Therefore, the key technical issue for reusable masks is how to recharge the middle layer of non-woven fabric and regenerate the electrostatic adsorption effect without destroying the mask material and microstructure.

Mask design examples:
Airtight design: The mask uses a large area of blue airtight fin edge. This seemingly thin blue material is the most technologically advanced part of the entire mask. It has a certain elasticity, extremely high airtightness and hydrophobicity through the combination of elastic rubber and fabric layers. When worn, regardless of whether the size of the mask is suitable for the user's face shape, this layer of blue fin edge can fill the gap between the two. The folded edge fits the curve of the face tightly, distributing the same pressure to a larger contact area, making the pressure smaller and achieving a more comfortable wearing experience. At the same time, it greatly reduces the risk of leakage caused by gaps caused by contact with the facial surface. Therefore, in principle, this style of mask only requires one size.
Mask frame design: The PP material frame has a certain elasticity, which provides a larger space inside the mask after propping up the mask, greatly increasing the breathing buffer space. At the same time, the mask filter material will not bulge or deflate with breathing, and the mouth or nose bridge will not touch the inside of the mask.
Use of multi-layer filter material: multi-layer filter material design, four-layer composite structure. The two outermost layers are non-woven fabric layers that have no filtering ability and mainly protect the inner filter material. The two middle layers are white melt-blown fiber layers. Melt-blown fibers are very dense, and manufacturers usually charge them with electrostatic charges to filter and retain fine particles through physical blocking and electrostatic adsorption. Compared with the common single-layer melt-blown fiber layer, if two layers of coarse and fine melt-blown fibers are used, the filtration rate should be higher than that of a single layer.
Nose clip design: A polyurethane nose clip that is more suitable for Asian noses can be used. Compared with the common large-area metal nose clip, the white polyurethane nose clip is smaller and non-toxic and environmentally friendly, so it can better fit the generally low nose bridge of Asians and reduce the environmental burden. Two unique sponge bulging nose pads are specially set on the inner side of the nose clip, which just fills the most leaky position on both sides of the nose when wearing a mask.
Headband design: The common metal nail fixed headband has the risk of allergies. The ultrasonic welding headband adopts a top-to-bottom connected design, and users can more easily find a comfortable wearing angle and tension by adjusting the top and bottom synchronously. At the same time, this design also takes into account the wearing needs of users who wear glasses, avoiding the embarrassment of general elastic rubber band masks being broken or bounced on the face when worn.
2. What are the differences between different masks?
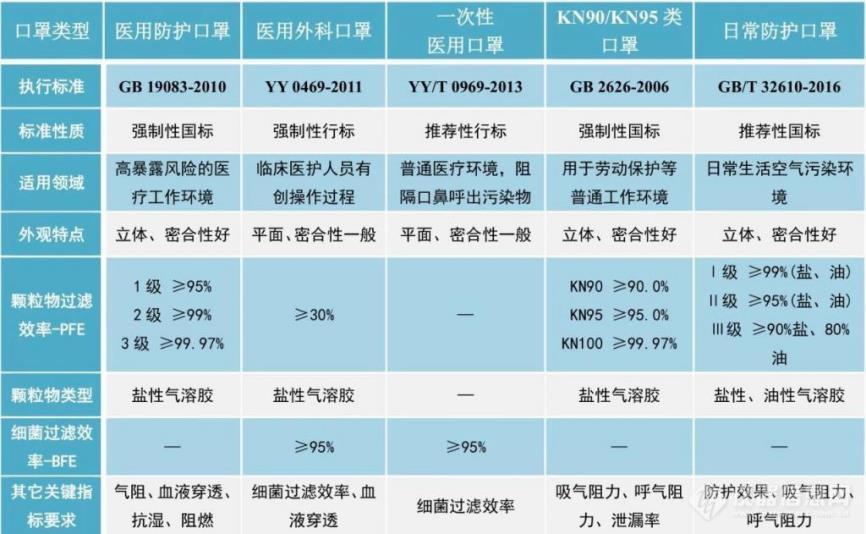
What are the differences between medical protective masks and ordinary N95 protective masks?
Medical protective masks are protective masks designed and approved by the government to protect medical workers in specific medical environments. Both medical protective masks and ordinary N95 protective masks have the function of respiratory protection against particles suspended in the air. However, there are additional requirements for protective masks used in medical environments. On the one hand, when medical staff perform surgery or treatment on patients, in order to prevent infection of patients, the medical masks they wear must be able to block the droplets and bacteria generated by the wearer's breathing and speaking from entering the surgical environment, and the masks themselves must also be hygienic, so the number of microorganisms on the original masks cannot exceed the standard, and exhalation valves are not allowed on the masks; on the other hand, in order to prevent the high-pressure infectious body fluids generated during surgery or treatment from splashing onto the mask and then penetrating into the wearer's mouth and nose, causing medical staff to be infected, medical masks must have the ability to resist the penetration of pressurized blood and body fluids. These two requirements are actually the main requirements for medical surgical masks. Medical protective masks must have the functions of both ordinary N95 protective masks and medical surgical masks, while ordinary N95 protective masks do not need to have the blood and body fluid penetration resistance and microbial control requirements of medical surgical masks and medical protective masks. Therefore, it is a misunderstanding to think that only medical protective masks can prevent bacteria and viruses. In addition to medical workers using them to protect against high-pressure body fluid splashes, ordinary N95 protective masks or masks with equivalent performance can be used for protection.

KN95 mask, N95 mask
Are protective masks with exhalation valves available?
The function of the exhalation valve is to reduce the exhalation resistance of the protective mask. Medical protective masks are not allowed to be equipped with exhalation valves because an open exhalation valve may discharge droplets or bacteria produced by the mask wearer out of the mask, which may threaten the patient undergoing surgery. Therefore, if you wear a protective mask to help yourself prevent viruses, it is no problem to choose a more comfortable protective mask with an exhalation valve; but if a person suspects that he or she is infected or has been infected by a virus, he or she should take the initiative to wear a mask without a breathing valve. The benefit of this is that it protects both yourself and avoids infecting others.
Are knitted masks effective in protection?
Knitted masks, as the name implies, are masks made from knitted fabrics. Currently, many knitted masks on the market are tested according to the FZ/T 73049-2014 standard. The main test types and bases are:
GB/T 2910 (all parts) Quantitative chemical analysis of textiles
GB/T 2912.1 Determination of formaldehyde in textiles - Part 1: Free and hydrolyzed formaldehyde (water extraction method)
GB/T 3920 Textiles - Tests for colour fastness - Colour fastness to rubbing
GB/T 3921—2008 Textiles - Tests for colour fastness - Colour fastness to washing with soap
GB 9994 Standard moisture regain of textile materials
GB/T 17592 Determination of banned azo dyes in textiles
GB 18401 National Basic Safety Technical Specifications for Textile Products
FZ/T 01057 (all parts) Test methods for identification of textile fibers
FZ/T 01095 Test method for spandex fiber content in textiles
GSB 16-2500 Knitted fabric surface defect color sample 3 specifications
The main test contents include internal quality and appearance quality. Internal quality includes pH value, formaldehyde content, odor, decomposable carcinogenic aromatic amine dyes, fiber content, color fastness to soaping, color fastness to water, color fastness to saliva, color fastness to friction, color fastness to perspiration, air permeability and other indicators; appearance quality includes surface defects, sewing regulations and other indicators. The internal quality requirements are shown in the following table.
As a knitted mask, if you want to achieve a better protective effect, it is recommended that in addition to referring to the general textile standard "FZ/T 73049-2014", you should also choose a mask that has the national mask protection standard GB2626-2006 testing indicators. Only masks that pass the test can play a protective role.
Are antibacterial masks really antibacterial?
The use environment of medical surgical masks requires that the masks have the function of blocking bacteria from penetrating. The industry standard requires that the bacterial filtration efficiency of masks reach more than 95%. Bacterial filtration efficiency detection method: The bacterial filtration efficiency test uses Staphylococcus aureus to make a bacterial suspension, and uses an aerosol generator to generate bacterial aerosols. After the aerosol is filtered through the mask, the filtered bacteria are collected with a six-stage Anderson sampler. After cultivation and colony counting, the number of bacteria that pass through the mask and are not blocked is obtained as the test group data. It is compared with the positive control group that does not pass through the mask and directly collects bacteria in the aerosol by the sampler to obtain the bacterial filtration efficiency of the mask. In the actual test process, there are specific requirements for bacterial liquid concentration, aerosol flow, sampling time, etc., and the colony count needs to be corrected to ensure the authenticity and reliability of the experimental results.
The new version of the YY 0469-2011 standard adopts a new bacterial filtration efficiency test system, which is an innovative improvement on the 2004 version of the traditional test system. It adopts a dual-gas-path simultaneous comparative sampling method, that is, the test group and the positive control group simultaneously collect the number of bacteria in the same aerosol. This synchronous sampling method improves the sampling accuracy and test efficiency, and the new test system adopts a negative pressure design as a whole to ensure the safety of operators.
The technical requirements for filtration efficiency in the new version of the industry standard YY 0469-2011 "Technical Requirements for Medical Surgical Masks" are non-oily particle filtration efficiency ≥ 30%, and bacterial filtration efficiency ≥ 95%, among which the non-oily particle filtration efficiency requirement is lower and the bacterial filtration efficiency requirement is higher. The test results show that when a mask meets both requirements at the same time, the non-oily particle filtration efficiency value is often much higher than 30%, and the test results are significantly positively correlated. According to the test results, when the product has a higher non-oily particle filtration efficiency, the feasibility of using the particle filtration efficiency result to replace the bacterial filtration efficiency can be further considered, that is, when the particle filtration efficiency value (PFE) of the medical surgical mask is higher than the specified value, such as 85%, the bacterial filtration efficiency test can no longer be performed, which can not only reduce the risk of harm caused by the use of pathogenic microorganisms in the laboratory, but also save inspection resources and improve inspection efficiency.
3. Mask Regeneration and Reuse Operation
Hot water disinfection: Soak the used disposable medical non-woven mask in hot water above 56°C for 30 minutes (refer to the "New Coronavirus Pneumonia Prevention and Control Plan (Fourth Edition)" 56°C for 30 minutes can effectively inactivate the virus), inactivate the new coronavirus, and wash away dust. Hang the mask to dry or air dry after washing. [Usually, boiling water and room temperature water (calculated at 20°C) are mixed in a 1:1 volume ratio at about 60°C. To improve the disinfection and sterilization effect, the boiling water ratio can be appropriately increased. Note: Do not rub the mask during hot water disinfection and washing to avoid damaging its microstructure; it is best to soak it in a pot of hot water per person to avoid cross contamination. ]
Charge regeneration: Place the mask flat on a dry, insulating surface after hanging/drying, and blow it with a hair dryer for 10-20 minutes, with the air outlet about 10 cm away from the mask (pay attention to the outlet temperature of the hair dryer, do not set it too high to avoid burning the mask fiber, and imitate the process of drying your hair after shampooing). Alternatively, use an ordinary electric fan to blow the mask for about 20 minutes, at a distance of about 5 cm. Or use an ordinary household electronic igniter or other static electricity generator to "shock" the mask to fully cover it, so that the mask can be recharged.
Paper scraps test: Sprinkle some dry paper scraps on an insulated tabletop, and bring the outer layer of the regenerated mask close to the paper scraps. When the distance is greater than 1 mm but not in direct contact, the mask can be observed to adsorb the paper scraps with static electricity, indicating that the mask has sufficient charge and can be reused. [If the static adsorption phenomenon is not obvious, extend the processing time of the second step of charge regeneration, and test the charge of the regenerated mask through "paper scrap adsorption" again until the charge is sufficient and can be reused.]
Reprinted from: [Instrument Information Network]
Please leave us a message
Jinan Shengtai Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise specializing in the research, development, production and sales of new laboratory analytical instruments, online atmospheric monitoring equipment and laboratory intelligent pretreatment equipment.
Log in to view more information
Log in to view more information

